G80 Forged European Type / US Type Master Link Assembly with Flat
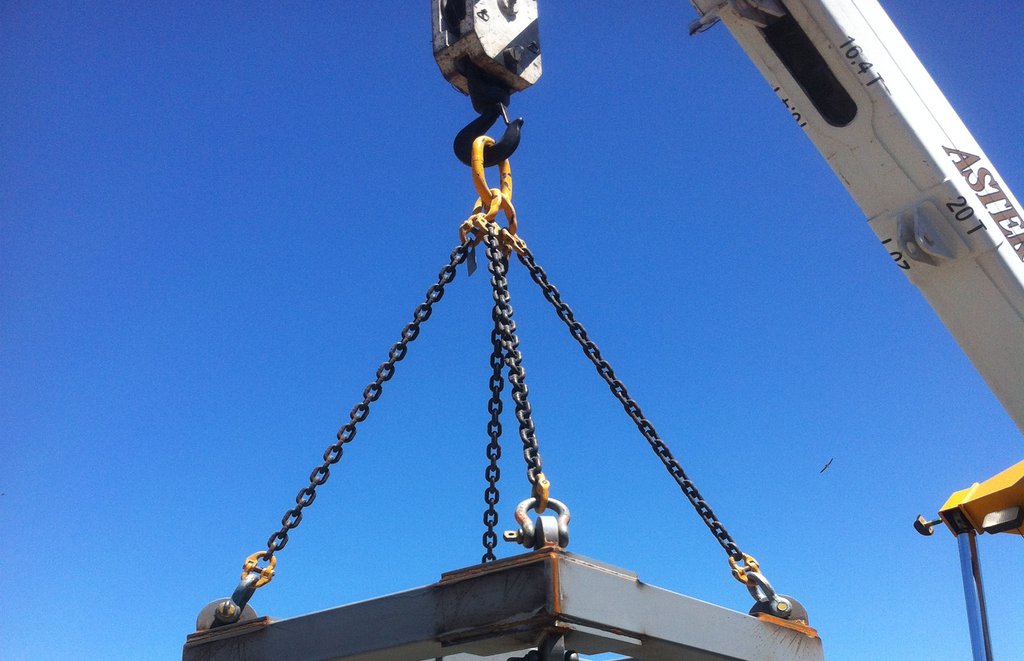
In the world of heavy lifting and rigging, ensuring the safety and efficiency of equipment is paramount. One of the critical components in such operations is the G80 Master Link Assembly. This assembly plays a crucial role in lifting applications, connecting chains, hooks, and other rigging hardware to the lifting equipment.
The G80 Master Link Assembly is a lifting component typically used in chain slings. It consists of one large master link and two or more sub-links (also known as intermediate or coupling links) that form a secure connection point for attaching multiple chain legs, hooks, or other lifting devices. The term “G80″ refers to the grade of steel used in the manufacturing of these components, with Grade 80 being a high-strength alloy steel known for its superior durability and load-bearing capacity.
Composition and Design
The G80 Master Link Assembly is forged from high-grade alloy steel, which is heat-treated to achieve optimal strength and durability. The master link, the primary component of the assembly, is oval or pear-shaped and designed to bear the load of the lifting operation. The sub-links are smaller in size and connect to the master link, allowing for multiple connections to be made.
The design of the G80 Master Link Assembly is critical to its function. The links are typically polished to reduce friction and resist wear, ensuring a longer lifespan even in harsh working environments. Additionally, each component is precision-engineered to meet strict safety standards, including those set by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
Applications of G80 Master Link Assemblies
The G80 Master Link Assembly is versatile and used across various industries, including construction, mining, oil and gas, and shipping. Its primary application is in chain sling assemblies, where it serves as the central connection point for multiple chain legs in multi-leg sling configurations (e.g., two-leg, three-leg, or four-leg slings).
Some specific applications include:
- Construction: Used in lifting heavy construction materials, such as steel beams, concrete blocks, and prefabricated components.
- Mining: Essential in lifting and moving large mining equipment and ore containers.
- Oil and Gas: Employed in offshore drilling rigs and platforms for lifting pipes, equipment, and other materials.
- Shipping: Used in loading and unloading cargo, particularly in situations requiring precise and secure lifting operations.
Advantages of Using G80 Master Link Assemblies
There are several advantages to using G80 Master Link Assemblies in lifting operations:
- High Load Capacity: The Grade 80 alloy steel provides excellent strength, allowing the assembly to handle heavy loads with ease. The load capacity is significantly higher compared to lower-grade materials.
- Durability: The heat-treated alloy steel is resistant to wear, corrosion, and impact, making it ideal for use in harsh environments where other materials might fail.
- Versatility: The ability to connect multiple chain legs to a single assembly makes it a versatile tool for a wide range of lifting applications.
- Compliance with Safety Standards: G80 Master Link Assemblies are manufactured to meet stringent safety standards, ensuring reliable performance and reducing the risk of accidents during lifting operations.
- Ease of Inspection and Maintenance: The design of these assemblies allows for easy inspection and maintenance, ensuring that any wear or damage can be detected early and addressed promptly.
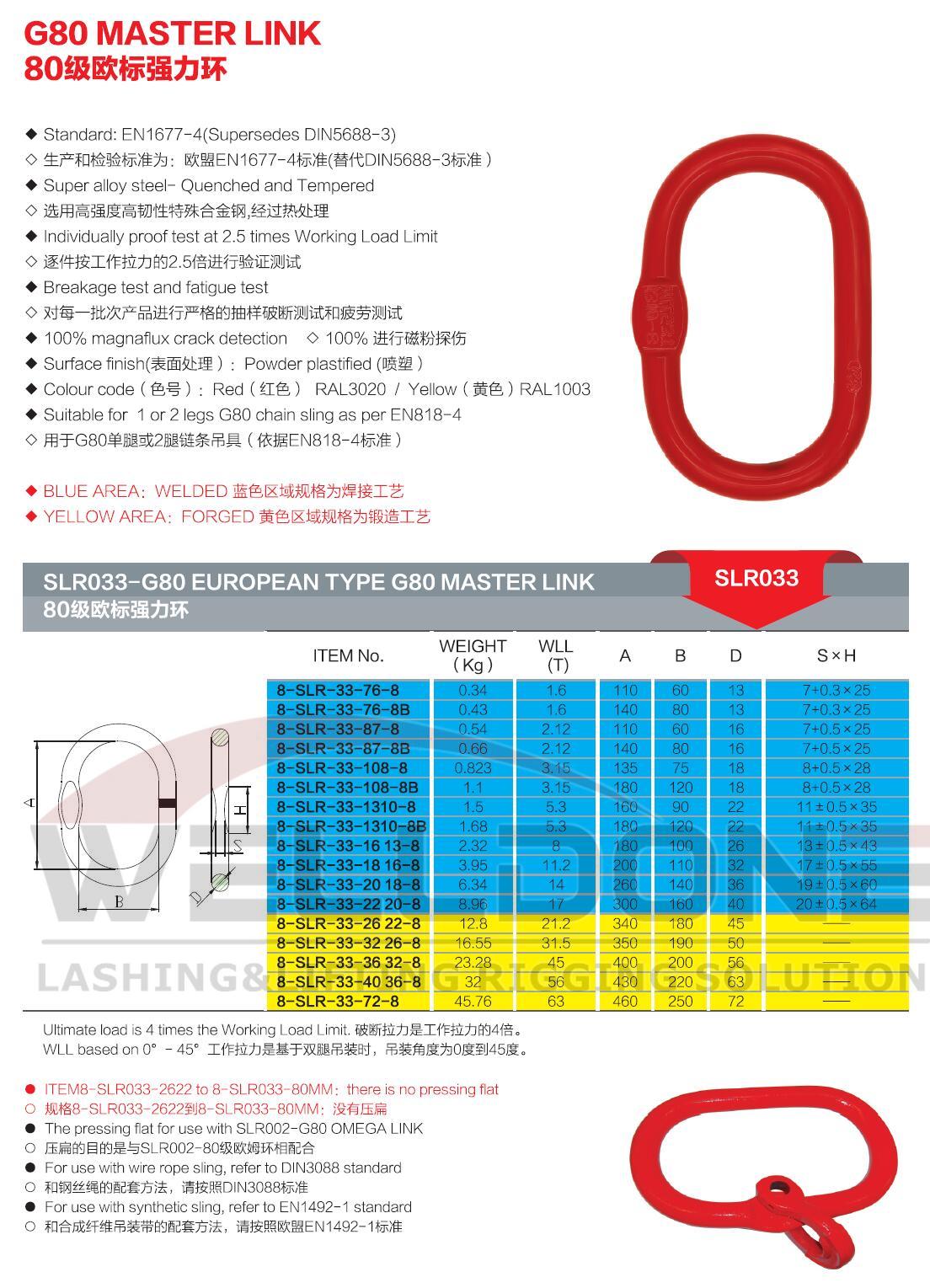
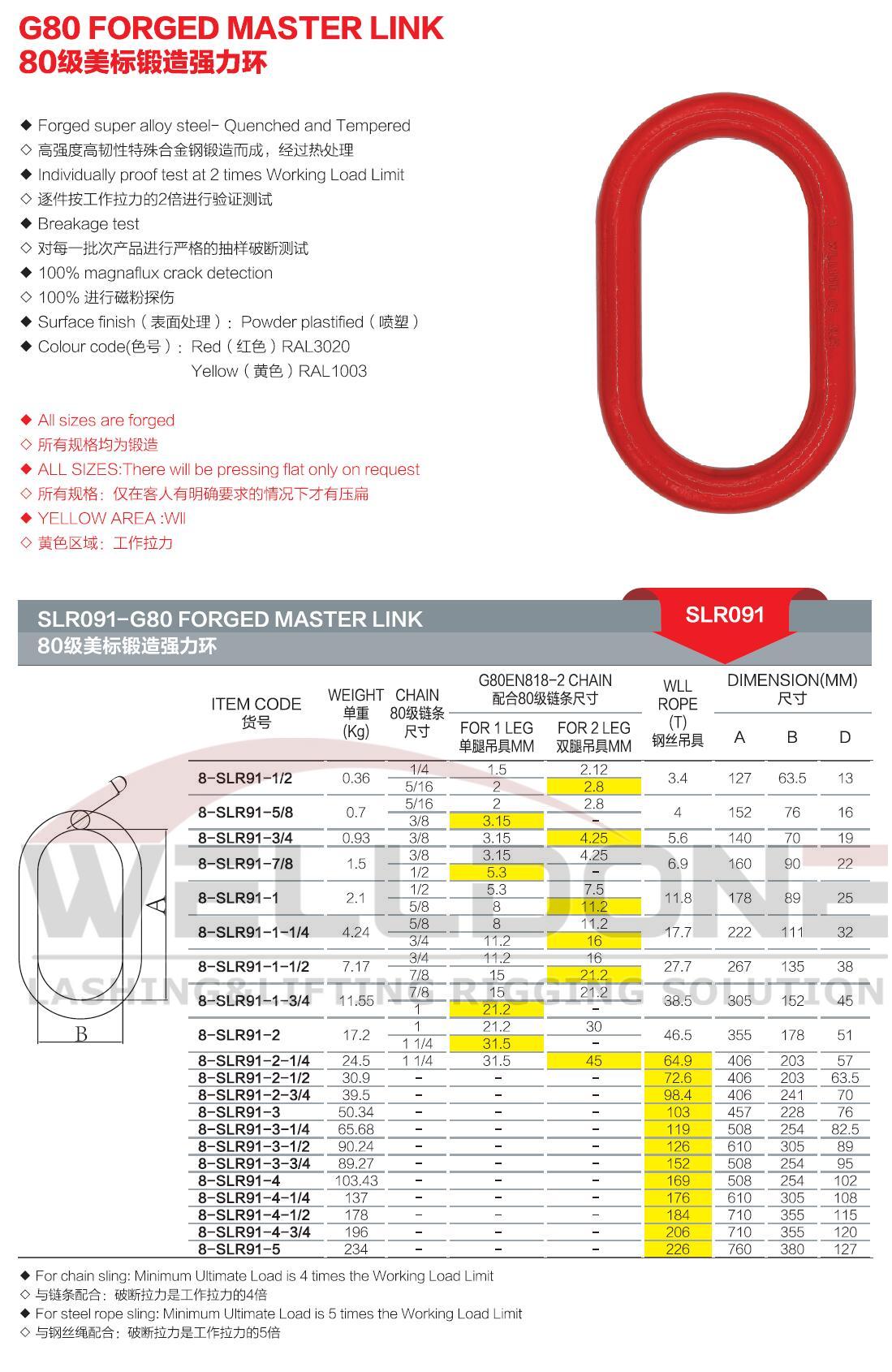
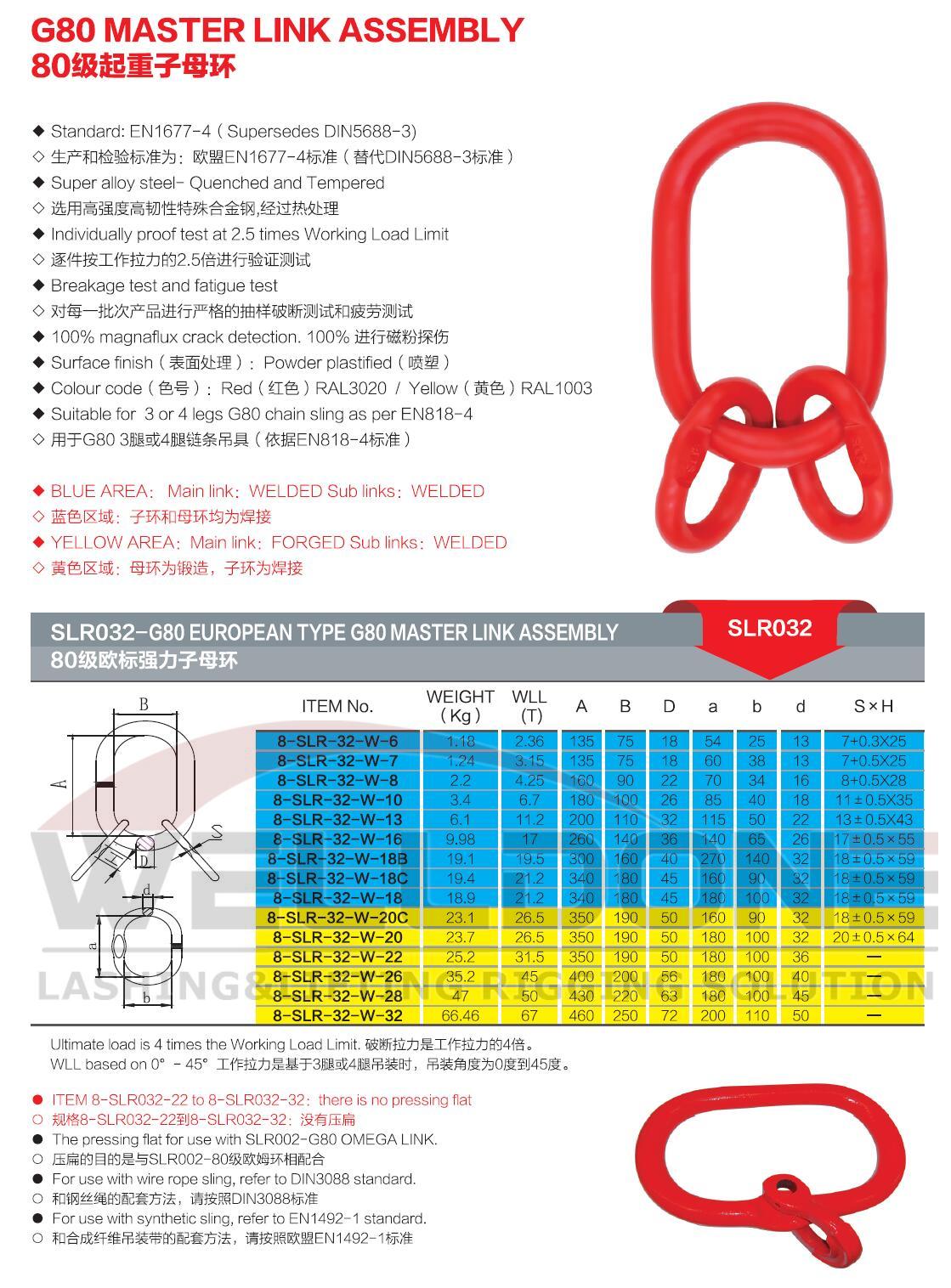
Model Number: SLR032/033/091/092
-
Cautions:
- Visual Inspection: Checking for signs of wear, deformation, cracks, or corrosion. Any indication of damage should be addressed immediately by replacing the affected components.
- Dimensional Inspection: Ensuring that the dimensions of the links remain within the manufacturer’s specified tolerances. Over time, repeated loading can cause elongation or distortion.
- Load Testing: Periodic load testing, as recommended by safety standards, to confirm that the assembly can still handle its rated load capacity.